Publications
Distributed Page Table: Harnessing Physical Memory as an Unbounded Hashed Page Table
57th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO 2024)
Osang Kwon*
Yongho Lee*
Junhyeok Park
Sungbin Jang
Byungchul Tak
Seokin Hong
Abstract
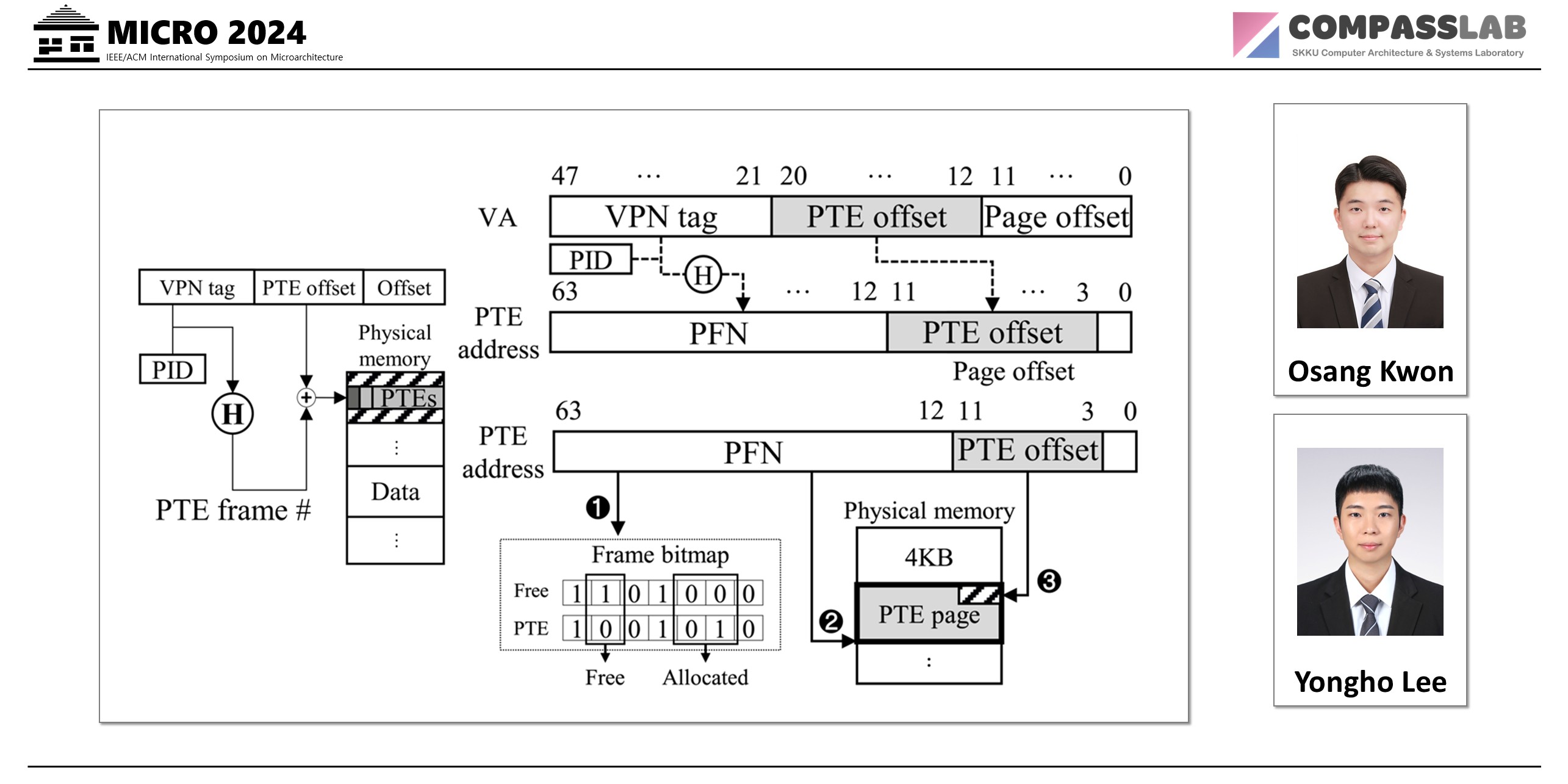
Virtual memory systems rely on the page table,a crucial component that maps virtual addresses to physical addresses (i.e., address translation). While the Radix Page Table (RPT) has traditionally been used for this task, its limitations have become more apparent with the rise of memory-intensive applications. Recently, Hashed Page Tables (HPTs) have been explored as an alternative page table structure to offer faster address translation. However, the HPT introduces its own set of challenges particularly in resizing the page table and allocating contiguous physical memory space for storing the table.To tackle the fundamental problem of the existing HPTdesigns, this paper introduces Distributed Page Table (DPT), a novel approach that utilizes the physical memory as a huge hashed page table. DPT distributes Page Table Entries (PTEs) across the entire physical memory space, significantly reducing the hash collisions while avoiding the table resizing overheads.When distributing the PTEs across the physical memory, they can be mapped to memory locations already allocated to data pages.This new type of collision, referred to as address collision, may reduce the effectiveness of the DPT. This paper showcases that the DPT can effectively resolve the address collision with three simple yet efficient techniques: Strided Open Addressing (SOA), Collision-Aware Virtual Address Allocation (CVA) and Collided Page Displacement (CPD). Our experimental results demonstrate that DPT achieves average performance improvements of 12.6%, 11.6%, and 8.7% compared to traditional RPT, the latest largecoverage TLB design, and state-of-the-art HPTs, respectively.
Keywords