Publications
LibraPIM: Dynamic Load Rebalancing to Maximize Utilization in PIM-Assisted LLM Inference Systems
2025 International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques (PACT 2025)
Hyeongjun Cho
Yoonho Jang
Hyungi Kim
Seongwook Kim
Keewon Kwon
Gwangsun Kim
Seokin Hong
LibraPIM: Dynamic Load Rebalancing to Maximize Utilization in PIM-Assisted LLM Inference Systems
“Balance is the New Speed”
The proliferation of Large Language Models (LLMs) has been a key driver of the AI revolution, and to run them efficiently, modern systems use heterogeneous architectures that combine xPUs (like GPUs/NPUs) with Processing-in-Memory (PIM). However, a key problem persists: static and coarse-grained workload allocation leads to a significant imbalance. This leaves one device idle while the other is overworked, even with techniques like batch pipelining. This underutilization is a major bottleneck for efficient LLM inference.
The Problem: Workload Imbalance in Heterogeneous System
Modern AI inference, which has both memory-intensive and compute-intensive characteristics, is a promising area for heterogeneous systems that combine xPUs and PIM. However, a fundamental challenge arises from the unbalanced workload between these components. The computational load for memory-intensive tasks and compute-intensive tasks is not always equal, as it varies significantly with model and input characteristics. This imbalance inevitably overburdens one device while leaving the other idle, leading to significant underutilization and a corresponding drop in performance.
Furthermore, PIM-enabled systems face a specific challenge: resource contention within DRAM banks. Since PIM must perform both computation and memory operations simultaneously, different tasks can end up mutually blocking each other. This contention forces inefficient solutions, such as duplicating resources (e.g., making the bank size larger by over 50%) or using time interleaving, both of which introduce significant overhead.
The Proposed Solution: LibraPIM, A Dynamic Heterogeneous PIM Framework
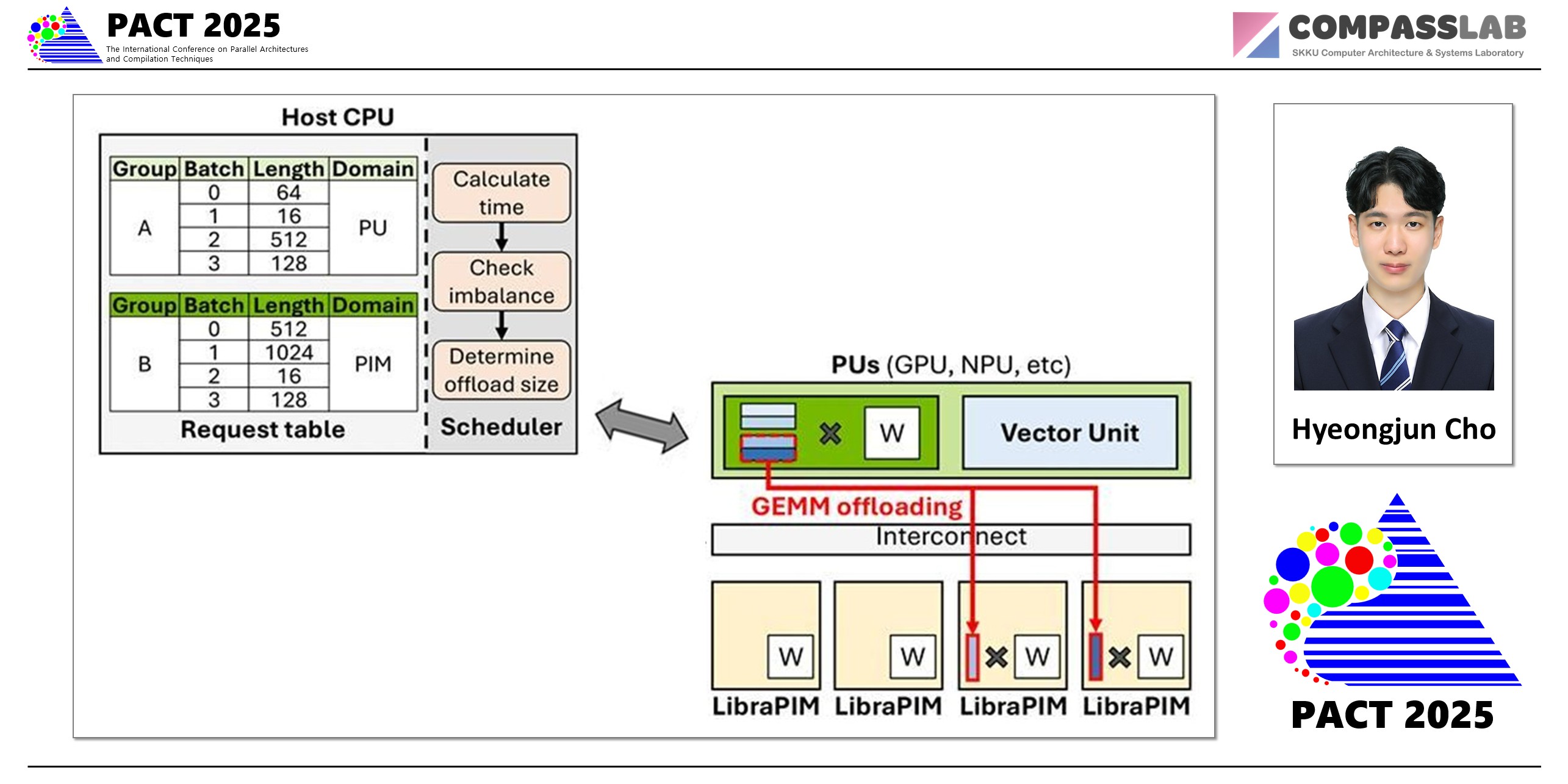
To solve the problems of these xPU-PIM heterogeneous systems, this paper introduces LibraPIM, a dynamic heterogeneous PIM framework. LibraPIM analyzes the operations of an imbalanced workload and dynamically distributes the workload through a device-aware scheduler. Furthermore, it proposes an architecture that enables low-cost parallel execution through DEX (Dual-Path Execution).
The key idea is simple yet powerful:
Dynamic Batch Offloading (DBO): LibraPIM features a runtime scheduler that predicts the workload of each device. When an imbalance is detected, it dynamically offloads a portion of the workload in a fine-grained manner from the bottlenecked device to its idle partner. Unlike conventional allocation, this adaptive approach allows for flexible task-device offloading, enabling the PIM to assist with GEMM operations or the xPU to handle GEMV tasks when it is beneficial.
Dual-Path Execution (DEX): This is enabled by Dual-Path Execution (DEX), a lightweight hardware modification. By physically partitioning each DRAM bank into two independent sections using slicing transistors, DEX creates separate data paths for xPU memory access and PIM computation. This design allows both operations to execute concurrently, eliminating the resource conflicts and idle time found in conventional systems. Remarkably, this is achieved with a negligible area overhead of just 0.032%.
The Impact: Overcoming Underutilization makes Performance Gains
By minimizing idle time and maximizing resource utilization, LibraPIM unlocks significant performance gains across the board. The evaluation demonstrates that LibraPIM:
Achieves an average 6.2x speedup over baseline PIM-assisted systems.
Delivers a 2.1x average speedup compared to the state-of-the-art heterogeneous approach.
Increases device utilization dramatically, achieving up to 38% for PIM and 77% for the NPU.
LibraPIM resolves a critical efficiency problem in modern AI inference hardware. By ensuring that all computing resources work together in a balanced and coordinated symphony, it paves the way for faster, more scalable, and more efficient LLM services.
Keywords